Абстракция в пространстве
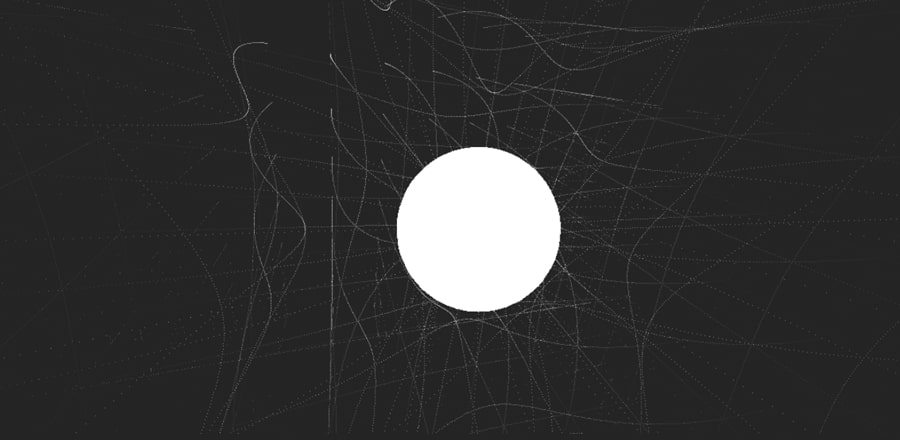 Абстракция на three.js и шейдерах
Абстракция на three.js и шейдерахHTML & Shaders
<script type="x-shader/x-vertex" id="vertexshader">
precision highp float;
attribute float size;
uniform vec4 planet1;
uniform vec4 planet2;
varying float vDisplay;
varying float vColor;
vec4 distanceTo(vec3 p1, vec4 p2){ // simple function that returns a vec4 of the distance between 3d points. each position being that axis' distance. the 4th position being the overall distance
vec3 d = vec3(p2.x - p1.x, p2.y - p1.y, p2.z - p1.z);
return vec4(abs(d.x),
abs(d.y),
abs(d.z),
sqrt(d.x*d.x + d.y*d.y + d.z*d.z));
}
void main() {
vec3 p = position;
float g = 5000.; // constant rate of gravity, I treat it sort of like a scaler
vec4 distP1 = distanceTo(p, planet1); // get distance from point to planet
//vec4 distP2 = distanceTo(p, planet2);
vec3 vp1 = vec3(p.x - planet1.x, p.y - planet1.y, p.z - planet1.z); // find vector between point and planet (kind of like the angle between the two points)
//vec3 vp2 = vec3(p.x - planet2.x, p.y - planet2.y, p.z - planet2.z);
float pull = (g*planet1.w) / (distP1.w * distP1.w); // find the amount gravity is effecting this point
vec3 newp = p.xyz + (-pull * vp1.xyz); // push the point towards the planet with the "angle" vector we made above, with the amount set in the pull variable
//pull = (g*planet2.w) / (distP2.w * distP2.w);
//newp = newp.xyz + (-pull * vp2.xyz);
gl_PointSize = 1.;
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(newp, 1.0);
vDisplay = 0.;
if(pull < 1.){ vDisplay = 1.; } // hide overly-pulled vertex's
vColor = clamp(pull, 0.133333333, 1.);
}
</script>
<script type="x-shader/x-fragment" id="fragmentshader">
uniform sampler2D texture;
uniform vec2 resolution;
varying float vDisplay;
varying float vColor;
void main() {
vec2 st = gl_FragCoord.xy/resolution.xy;
st.x *= resolution.x/resolution.y;
float c = clamp(vColor, 0.0, 0.4);
gl_FragColor = vec4(c, c, c, vDisplay );
}
</script>CSS
html, body {
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
background-color: #222;
display: flex;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
}
canvas {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}JS
Библиотека three.jshttps://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/three.js/86/three.min.js/*
The main logic in this app is in the HTML tab
within the Vertex Shader code
*/
var container = document.body;
var scene = new THREE.Scene();
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, container.offsetWidth / container.offsetHeight, 0.1, 1000000 );
var uScale = container.offsetWidth / 178960000*80000;
var renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ alpha: true });
renderer.setSize( container.offsetWidth, container.offsetHeight );
container.appendChild( renderer.domElement );
var startTime = new Date().getTime();
var currentTime = 0;
var planetGeom = new THREE.SphereGeometry( Math.floor(6371*uScale), 32, 32 );
var planetMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( {color: 0xffffff} );
var planet1 = new THREE.Mesh( planetGeom, planetMaterial );
//planet1.mass = 0;
planet1.mass = 59720*uScale;
scene.add( planet1 );
var planetGeom = new THREE.SphereGeometry( Math.floor(1737*uScale), 32, 32 );
var planetMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( {color: 0xcccccc} );
var planet2 = new THREE.Mesh( planetGeom, planetMaterial );
planet2.dist = 384400*uScale;
planet2.mass = 735*uScale;
//scene.add( planet2 );
// adding in multi-planet support (almost there)
var geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
var uniforms = {
time: { value: 1.0 },
resolution: { value: new THREE.Vector2(container.offsetWidth, container.offsetHeight) },
planet1: { value: new THREE.Vector4(planet1.position.x, planet1.position.y, planet1.position.z, planet1.mass) },
planet2: { value: new THREE.Vector4(planet2.position.x, planet2.position.y, planet2.position.z, planet2.mass) }
}
var shaderMaterial = new THREE.ShaderMaterial( {
uniforms: uniforms,
vertexShader: document.getElementById('vertexshader').textContent,
fragmentShader: document.getElementById('fragmentshader').textContent,
blending: THREE.AdditiveBlending,
depthTest: false,
transparent: true,
vertexColors: true
});
var pointDist = 1;
var lineScale = 50;
var scale = Math.floor(64*8);
var radius = Math.floor(196);
var geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
var positions = [];
var sizes = [];
function mod(x,y){
return x % y;
}
for ( var x = 0; x + pointDist < scale; x += pointDist) {
for ( var y = 0; y + pointDist < scale; y += pointDist) {
for ( var z = 0; z + pointDist < scale; z += pointDist) {
if((mod(x, lineScale) < 1. && mod(y, lineScale) < 1.) || (mod(y, lineScale) < 1. && mod(z, lineScale) < 1.) || (mod(x, lineScale) < 1. && mod(z, lineScale) < 1.)){
positions.push( (x - (scale/2)) * radius );
positions.push( (y - (scale/2)) * radius );
positions.push( (z - (scale/2)) * radius );
sizes.push( 1 );
}
}
}
}
geometry.addAttribute( 'position', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute( positions, 3 ) );
//geometry.addAttribute( 'sPosition', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute( positions, 3 ) );
geometry.addAttribute( 'size', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute( sizes, 1 ).setDynamic( true ) );
var spacetime = new THREE.Points( geometry, shaderMaterial );
spacetime.position.x = 0;
spacetime.position.y = 0;
spacetime.position.z = 0;
scene.add( spacetime );
camera.position.y = 0;
camera.position.x = 0;
camera.position.z = 20000;
function animate() {
var now = new Date().getTime();
currentTime = (now - startTime) / 1000;
uniforms.time.value = currentTime;
planet1.position.x = Math.cos(currentTime)*2000;
planet1.position.y = Math.sin(-currentTime)*2000;
planet2.position.x = planet1.position.x + Math.cos(currentTime)*planet2.dist * uScale;
planet2.position.y = planet1.position.y + Math.sin(currentTime)*planet2.dist * uScale;
uniforms.planet1.value = new THREE.Vector4(planet1.position.x, planet1.position.y, planet1.position.z, planet1.mass);
uniforms.planet2.value = new THREE.Vector4(planet2.position.x, planet2.position.y, planet2.position.z, planet2.mass);
scene.rotation.z += 0.0002;
scene.rotation.y += 0.001;
requestAnimationFrame( animate );
renderer.render( scene, camera );
}
animate();